The public is largely disenchanted with the way the federal No Child Left Behind Act measures student learning and teacher quality, and it would like greater input into the law’s implementation, a report scheduled for release this week by the Public Education Network finds.
The report from PEN, a Washington-based advocacy group of individuals and more than 80 local education funds around the country, is based on a series of public forums conducted in 10 states from fall 2005 through this past January. The meetings, which were modeled on congressional hearings, were attended by about 250 people each and held primarily in cities with a large number of Title I schools, including New York City, Orlando, Fla., and Austin, Texas.
Missing Voices
Federal Title I aid for schools with needy students is used in carrying out many provisions of the 4-year-old No Child Left Behind law, which was an overhaul of the Elementary and Secondary Education Act.
The report, drawn from the sessions, was intended to give a voice to students, parents, and community groups, who were left out of the process of drafting the NCLB law in 2001, said Arnold F. Fege, the director of public engagement and advocacy for PEN.
The Public Education Network received 8,000 responses to an online survey it conducted last fall, including to the question of whether the No Child Left Behind Act requires “too much testing, too little, or just right?”
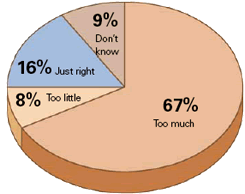
SOURCE: Public Education Network
“When the NCLB table was set, parents and the community were missing from the table, and we’re now paying the price,” Mr. Fege said. Such groups should have a broader role in the reauthorization of the current law, which Congress is scheduled to begin working on next year, he said.
While many parents and students lauded the law’s goal of bringing more accountability to public education, they questioned the “adequate yearly progress” model, which requires states to meet yearly targets for the percentage of students scoring at least proficient on reading and math tests.
People at the forums dismissed the idea that “a single test can create an accurate portrayal of how well a school is performing,” the report says. Instead, many recommended using tests to measure how much students have learned from one year to the next, sometimes called “growth” models.
Mr. Fege noted that U.S. Secretary of Education Margaret Spellings has allowed some states to participate in a “growth model” pilot program, which allows states to get credit for students who make academic progress from year to year, even if they do not become proficient. But he said many parents and community members would like to see such an approach applied nationwide. (“U.S. Pilot of AYP ‘Growth’ Models Advances,” April 12, 2006)
More Coordination Sought
Some forum participants also suggested that the law’s definition of “highly qualified” teachers, which requires educators to meet state and federal standards for teaching skill and content knowledge, may need to be expanded. They said teacher preparation should include training educators to reach students from diverse backgrounds and with varying learning styles. The report recommends that financial incentives, including extra pay, tax credits, and student-loan forgiveness, be used to attract effective teachers to lower-performing districts.
The report suggests that the federal government require more coordination among schools and social-service agencies, both for higher-performing and for struggling districts.
It also recommends that the law’s parental-involvement provisions be strengthened to give parents more say in school improvement, possibly adding a complaint procedure for parents who believe their districts are not complying with the law.
Michael J. Petrilli, the vice president for national programs and policy at the Thomas B. Fordham Foundation, a Washington-based organization that supports accountability and choice in education, said low-performing schools may also need more governance authority, including for dealing with personnel issues.
“If you can make [more community involvement] work, of course, that’s great,” he said, noting that his organization supports charter schools, which he said are often based on community and parental involvement.
But Mr. Petrilli, who served as a U.S. Department of Education official from 2001 to 2005, added: “Our experience has been that support is not enough. … Schools are failing because of politics.”
He noted that the least-qualified teachers often work in the lowest-performing schools, a point the PEN report also makes. But some schools might need more power to remove ineffective teachers and gain concessions from their unions, he added.
The report, which was scheduled for release May 1, is the second in a series of PEN reports on the NCLB law. The first, released in March 2005, found that parents were concerned about funding and resources for the law and about the level of information available about it, among other issues.








