A new study on gender differences in academic achievement, offering what it calls “good news for girls and bad news for boys,” finds that, overall, male students in every state where data were available lag behind females in reading, based on an analysis of recent state test results. At the same time, in mathematics, a subject in which girls have historically trailed, the percentages of both genders scoring “proficient” or higher were roughly the same, with boys edging out girls slightly in some states and girls posting somewhat stronger scores in others.
In certain states, such as Arkansas, Hawaii, New Mexico, and Vermont, the gender gap for reading proficiency was 10 percentage points or higher, based on 2008 test data, concludes the report, released this month by the Center on Education Policy, a Washington-based research group.
In a conference call with reporters, Jack Jennings, the group’s president and chief executive officer, noted that whether looking at student outcomes at the elementary, middle, or high school level, male rates of proficiency were lower than for females across all states studied in 2008. (Forty-five states had data available for all three levels.)
“This is no fluke,” he said. “There is a consistent achievement gap. ... Something is going on in our schools holding back boys.”
An analysis of state test results from 2008 indicates that male students are behind their female counterparts in every state in reading proficiency.
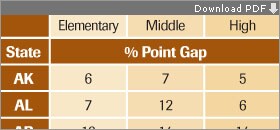
SOURCE: Center on Education Policy
The report does offer some encouragement for boys in reading, suggesting that as a group, they are making some gains over time, and that the gender gap has narrowed in many states.
For instance, in 38 out of 44 states, the percentages of 4th grade boys scoring proficient or higher climbed between 2002 and 2008. Also, in 24 out of 44 states, the gender gap for 4th graders in the percentage of students scoring proficient or higher narrowed over that time period, though it widened in another 14 states.
When looking at the data another way, however, based on changes in the average of test scores, the gaps between boys and girls in reading “widened across all three grade levels [elementary, middle, and high school] as often as they narrowed,” the study says.
‘Clear and Startling’ Differences
The new report is part of a series of studies from the Center on Education Policy examining trends on state tests since 2002, when the federal No Child Left Behind Act was signed into law.
The center notes that one reason for the report’s focus on the rate of students deemed “proficient” is that the designation is the key indicator used to determine whether districts and schools have made adequate yearly progress under the federal law. But as the report emphasizes, each state uses its own tests to gauge proficiency and sets its own cutoff score for what it judges proficient.
The report says that research has long noted historical differences in the achievement of boys and girls in reading and math, though considerable recent research suggests there is no longer a gender gap in math. (“Stereotype of Mathematical Inferiority Still Plagues Girls,” Aug. 27, 2008.)
With its state-by-state analysis, the report is able to identify those states that appear to struggle the most with gender gaps in reading. In Arkansas, for instance, the gap was 13 percentage points at the elementary level and 14 percentage points at both middle and high school in 2008.
Mr. Jennings noted that even Massachusetts, a state known for its strong performance, has a sizable gender gap, at 13 percentage points for elementary students in 2008.
Some other states, however, such as Florida, Kansas, Nebraska, and Virginia, had much smaller reading gaps at all levels.
In most cases, the gender gap in state math achievement did not exceed 5 percentage points, the 2008 data show.
Tom Loveless, a senior fellow at the Brookings Institution, a Washington think tank, said he’s not surprised by the findings about boys in reading, though he cautioned that looking at the percentage of students deemed proficient can be misleading.
“It’s like saying, if we got everybody above the poverty line, we would have eliminated [income] gaps,” Mr. Loveless said.
Even so, he says the data appear consistent with some findings from the National Assessment of Educational Progress.
The reading results on NAEP for 2009, issued last week, show 4th grade boys with an average scale score of 218, compared with 224 for girls. The gap was larger, 11 points, in 2000, but the naep report said the newest results on the gender gap were not “significantly different” than in 1992.
At 8th grade, however, the report says the gender gap was smaller by a statistically significant margin compared with 1992, dropping from 13 points to 9 points.