A majority of teenagers in the United States reported becoming distracted when using digital devices in class, and it has some correlation with their academic performance, according to results from the 2022 Program for International Student Assessment.
The PISA questionnaire, which the Organization for Economic Development and Cooperation administers to 15-year-olds every three years, asked students how often they were distracted by using digital devices (such as smartphones, websites, or apps) during their math lessons and how often they were distracted by other students using those resources.
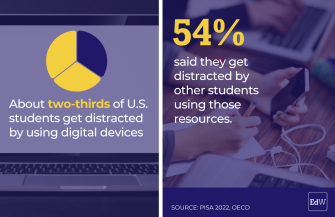
About two-thirds of U.S. students reported that they get distracted by using digital devices, and about 54 percent said they get distracted by other students who are using those resources, the PISA results found.
Those numbers are on par with the global average: 65 percent of students in countries that are part of the OECD said they get distracted by using digital devices, and 59 percent reported getting distracted by other students who are using digital devices.
These distractions show a strong correlation with lower academic performance, according to the report analysis. On average across OECD countries, students who said that they were distracted by other students using digital devices in class in at least some math lessons scored 15 points lower in mathematics than those who reported that this never or almost never happens.
The results “highlight the importance of finding effective ways to limit the distraction caused by using digital devices in class,” according to the report.
Many schools and districts in the United States have restricted student cellphone use during the school day because the devices have become an enormous distraction in the classroom. A Common Sense Media report found that teenagers receive a median of 273 notifications a day, with nearly a quarter coming in during school hours. U.S. lawmakers have introduced legislation that would require a study on the effects of cellphone use in schools on students’ mental health and academic performance.
In the Brush school district in Colorado, Superintendent Bill Wilson said part of the reasoning for restricting cellphone use during instructional hours in his district is to help students “focus on learning and take one element of distraction and disruption out of their life at least for the time that they were at school.”
However, most U.S. schools now also have 1-to-1 computing environments in which every student has a school-issued learning device, and those digital devices can be a distraction, too. It’s more challenging to completely restrict laptop use in class when much of student learning now happens online. Many educators are simply being more intentional about when and how they use digital devices in the classroom.
“We’re really working hard to be very mindful of what we choose to put kids on computers for,” said Kristy Zaleta, the principal of Rogers Park Middle School in Danbury, Conn. For instance, students can use their laptops to practice math lessons using personalized learning software, but that practice time is limited to 30-45 minutes per week in school. Other lessons revolve around physical manipulatives and hands-on activities, she said.
The following charts show how often students are distracted by their own use of digital devices as well as other factors related to students’ use of technology, according to the 2022 PISA data.







